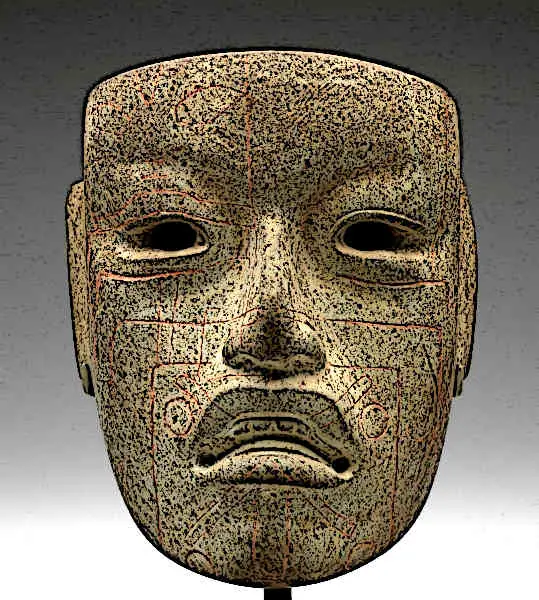
Olmec civilization was the earliest civilization that arose in the Mesoamerican regions. It was marked by its unique art and other long-living characteristics which left a deep influence on the subsequent civilizations in Mesoamerica.
Olmec civilization arose sometime around the 14th century B.C. and was first centered at San Lorenzo. It later shifted to La Venta where it existed until the 4th century when Olmec regions suffered depopulation and abandonment.
Olmec civilization was the first to practice ritual bloodletting in Mesoamerica. Although Olmec civilization did not practice human sacrifice, its culture of ritual sacrifice was inherited by later civilizations such as the Mayans and the Aztec.
Mayans began human sacrifices and practiced it a wide scale. Aztecs took it a step further and sacrificed thousands of humans annually.
Olmec civilization had a number of gods which the Olmec associated with animals. The animals they were commonly associated with included dragon, serpent and jaguar.
Later civilizations such as Mayans and Aztecs borrowed not only these characteristics of their deities from Olmecs but also exactly the animals that were associated with the gods.
Olmec created art in many forms, a significant portion of which is extant today in the form of little figurines. What is remarkable about Olmec art is that it is very naturalistic, depicting humans and other objects from daily life with unusual accuracy which is not found in other Mesoamerican civilizations.
One of the most extraordinary forms of Olmec art that has reached us are the colossal heads. These are huge heads carved out of volcanic rock, some of them as high as 11 feet, which are extant today.
A mystery surrounds the reason why the Olmec sculpted these heads or who they are meant to represent, although it has been speculated that they represent Olmec rulers.

Olmecs had an elite class which had more power and privileges than the common people. These elites were the main clients of the art, so art prospered because these elite could afford to buy it.
Olmecs had an intriguing sense of space and time. They believed that if any place led to a different direction in space or time, it was sacred. For this reason, caves which resembled a passage to the underworld were sacred.
Similarly, mountaintops which resembled a path to the heights of the gods were also considered sacred.
Olmec developed a writing system of their own which comprised of hieroglyphs. The oldest extant evidence of Olmec writing has been dated to 1100 B.C.
Olmec devised a sophisticated method by which they dyed a cylindrical seal and then imprinted it on any materials, such as animal skin or clothes. This helped them inscribe symbols easily.
In the 10th century, Olmec civilizations center migrated from San Lorenzo to La Venta. Archaeologists and historians are unable to determine what caused this migration from the first great city of the Olmec. San Lorenzo was not only abandoned but also suffered extensive destruction during the same century.
Olmec made no use of wheel and did not use any metal tools. Still, they were able to transport different kinds of rocks for tens of miles.
For the colossal heads cited above, Olmec transported rocks weighing up to 55 tonnes along distances of 50 miles and more. Doing this without the use of wheel was a remarkable feat of the Olmec civilization.
Artefact’s such as figurines and masks similar to the Olmec civilization have been found in cultures and civilizations hundreds of kilometers away from the Olmec heartlands.
This may have been because of the long-range trade that the Olmec conducted or simply because the Olmec culture was highly esteemed and cast a very strong influence over all other cultures in Mesoamerica.
Olmec made use of the concept of zero, which was remarkably advanced for their time.
They also created a Long Count calendar which became a permanent feature of all later Mesoamerican calendars, such as those of the Mayans and the Aztecs.

Ballgame has been the most popular sport all over Mesoamerica. The sport originated in the Olmec civilization and archaeologists have recovered rubber balls dating to 1600 B.C. near the heartland of the Olmec civilization.
Olmecs also had ball-courts to play the sport, and this architectural feature was also borrowed by later civilizations.
One of the possible reasons why Olmec were able to exert a cultural influence all over Mesoamerica was trade. Olmec conducted long-distance trade with different neighboring as well as remote regions.
This trade comprised of exotic and precious objects such as jade, obsidian, green-stone and seashells. Olmec civilization was among the first in the region to conduct trade at such a scale.
All Mesoamerican civilizations had maize as their staple diet. They cultivated maize at large scales and their food supplies depended on it. This trend also originated with the Olmec civilization.
Although the civilization originally began with a diverse diet but over time, Olmec began associating more and more significance with maize, so much so that it almost became a staple diet. In later Mayan and Aztec civilizations, maize assumed a religious importance.
This was another practice which originated with the Olmec civilization and then persisted throughout later Mesoamerican civilizations. Dogs were domesticated as animals for meat. So Olmec ate dogs as a common source of protein.
A number of rectangular altars have been discovered at the site of Olmec cities. Some of these depict a human figure holding a were-jaguar baby. Some have cited this as proof of infant sacrifice among the Olmec.
These altars are also a direct proof of the significance of jaguar as a ritualistic icon in the Olmec civilization.
Some recent researchers have claimed that Olmec had an African origin. Such claims have been based on the shape of the face carved in Olmec colossal heads. However, there is little proof to substantiate the claim that Africans had any connection with Mesoamerican in the pre-Colombian world.
